- Science & Research
- Science News
- Newsletter
- 2013
- July 12

Newsletter
Newsletter
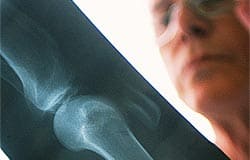
Deficient Vitamin D Levels Result In Early Aging Of Bone
Deficient vitamin D levels result in early aging of bone
Friday, July 12, 2013. In an article published online on July 10, 2013 in the journal Science Translational Medicine, researchers from University Medical Center in Hamburg, Germany and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory report a link between deficient levels of vitamin D and premature aging of the bone. The vitamin is needed for the absorption of calcium by bony tissue, as well as playing a role in many other processes. Björn Busse and his associates compared bone obtained from 15 normal individuals and 15 men and women with deficient serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels of less than 20 ng/mL and bone surface osteoidosis indicating the transition to osteomalacia. "The hallmark of osteomalacia is an excessive amount of unmineralized collagen matrix," Dr Busse and his colleagues explain. "The cause of this pathological accumulation of osteoid is difficult to determine and may result from a combination of an increased rate of bone formation, low serum calcium and phosphorus, and/or direct effects of the excess osteoid on osseous cells accompanied by changes in the bone matrix, either in the collagen or in the ground substance. As a consequence of the marked reduction in mineralized bone mass and increased amounts of osteoid, vitamin D–deficient bone represents a complex composite structure that is highly susceptible to fracture." Bone quality was analyzed on a scale ranging from nanometers to micrometers via the use of micro computed tomography. The researchers found that the increase in osteoid-covered surfaces in bone derived from deficient subjects impaired the remodeling of mineralized bone tissue underneath due to isolation from osteoclasts. These areas of bone continued to age and mineralize, exhibiting the structure of older bone tissue, which is more brittle than young bone. Further testing revealed that being deficient in vitamin D increased the initiation of cracks by 31% and their growth by 22%. "The assumption has been that the main problem with vitamin D deficiency is reduced mineralization for the creation of new bone mass, but we've shown that low levels of vitamin D also induces premature aging of existing bone," stated coauthor Robert Ritchie of Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory's Materials Sciences Division. "Our study expands the current clinical understanding of the pathophysiology of vitamin D deficiency and helps explain why well-balanced vitamin D levels are essential to maintain bone's structural integrity," the authors conclude. |
||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
BioPQQ® is a registered trademark of MGC (Japan) |
||||||||||||||||
The latest news on aging, nutrition, and vitamins
Lab
Testing
How Life Extension lab testing works