Life Extension Magazine®
Over 20 million Americans are estimated to have some form of peripheral neuropathy, a nerve disease that can lead to pain, numbness, and weakness, most often in the hands, feet, and legs.
Peripheral neuropathy has different causes, with diabetes and blood vessel problems notable among them.1
As it worsens, diabetic peripheral neuropathy may lead to the development of foot ulcers and the need for foot or leg amputations.2 People with peripheral neuropathy also have higher rates of overall mortality.3
But there’s good news. A nutrient called lipoic acid has been successfully used for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy in Germany for decades.4,5
Clinical trials in people suffering from diabetic neuropathy show that lipoic acid can reduce pain and other symptoms,6-9 and may help prevent progression of nerve damage.9
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?
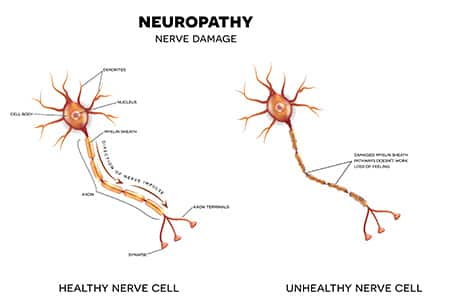
Peripheral neuropathy is a general term for disease of the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.10
Peripheral neuropathies, diabetic2,11 or non-diabetic, often begin in the feet, and often progress up the leg over time.1,12
Among other conditions that affect nerves, the most common culprit is high blood sugar, which is why people with type II diabetes have the highest rates of neuropathy.2,13
Estimates of the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in diabetics range as high as 70%.1
In adults without diabetes, peripheral neuropathy occurs much less frequently than in those with diabetes.13 Alcohol abuse, 13 some chemotherapy drugs,13 hereditary diseases, vitamin B12 deficiency, and other health conditions can contribute to or cause its development.1,14
Peripheral neuropathy often results in loss of function, numbness, tingling, and extreme pain. 12
Eventually, it may result in loss of balance.10 Diabetic neuropathy may result in difficulty walking and increased risk of falls. 5
Diabetic neuropathy is the major cause of diabetic foot ulcers and infections, which can lead to leg amputations.2,13 A large, clinical study showed lower-limb amputation rates in those with diabetes were 15 times higher than in non-diabetics.15
Neuropathy in diabetics can also affect nerves that control heart and blood vessels, causing abnormalities of heart rate and blood vessel function. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy can be associated with a high risk of arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death.16,17
One large study found that peripheral neuro-pathy is an independent predictor of higher overall mortality. 3
Lipoic Acid Defends Nerves
Lipoic acid is a compound produced in the body and also found in small amounts in some vegetables and animal products, particularly organ meats.18
It plays an essential role in turning glucose and other nutrients into energy.19 It enhances glucose uptake,20 and plays a role in modulating insulin sensitivity.21
It is also a potent antioxidant that helps fight oxidative stress. It even helps regenerate several other antioxidants. 12,22
One review reported that lipoic acid can help decrease pain signals by blocking channels on pain-sensing nerve cells.5
Lipoic acid has been licensed and used in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy for decades in Germany. 5
Easing Pain and Improving Function
Scientists have conducted many clinical trials of lipoic acid for diabetic peripheral neuropathy.6-9,18
Nerve conduction studies, which measure how efficiently electrical signals move through a nerve, have shown that lipoic acid can improve nerve function. Nerve conduction velocities that were previously slowed were boosted with lipoic acid use.8
Additional benefits have been identified in other trials.
For example, a clinical study in diabetics found that lipoic acid not only improved peripheral neuro-pathy scores, it also significantly decreased feelings of depression.9 Diabetics are two to three times more likely than non-diabetics to have depression.23
Another clinical study found that 50% of subjects felt their quality of life and overall health condition was “very much better” or “much better” following 40 days of lipoic acid supplementation.6
Studies have shown that lipoic acid led to improvements in potentially deadly cardiac autonomic neuropathy as well.8,24
Lipoic acid use has also been associated with improvements in body mass index,5,8,25 cholesterol levels,6 and markers of blood glucose control.8,24
What you need to know
Get Relief from Peripheral Nerve Pain
- Peripheral neuropathy is a common condition marked by loss of sensation, tingling, numbness, and pain in the peripheral nerves.
- The most common cause is high blood sugar, seen in type II diabetes, but people without diabetes can also suffer from peripheral neuropathy.
- Peripheral neuropathy is associated with an increased risk of overall mortality.
- The nutrient lipoic acid can help relieve peripheral neuropathy symptoms, including pain and numbness, and may also improve nerve function.
Summary
Peripheral neuropathy is a common condition that causes numbness, tingling, pain, and loss of function in the peripheral nerves. In diabetics, it is associated with an increased risk of amputations, falls, and death.
Lipoic acid has been used to treat diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Germany for decades.
Clinical studies show that it can lead to significant reductions in pain, numbness, and other symptoms.
Two Forms of Lipoic Acid
Lipoic acid occurs in two different forms: R-lipoic acid and S-lipoic acid.
Most production methods result in a mixture of these forms.18,26
The “S” form is not very biologically active. The “R” form is the biologically active component (and the kind produced by the body) that is responsible for lipoic acid’s phenomenal antioxidant effect.18,26
A lipoic acid formula that provides 100% R-lipoic acid can be readily used by the body, maximizing its health benefits.
Animal and human studies demonstrate that R-lipoic acid provides clinical benefits with much greater biological activity.18,26,27
If you have any questions on the scientific content of this article, please call a Life Extension Wellness Specialist at 1-866-864-3027.
References
- Available at: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/peripheral-neuropathy-fact-sheet. Accessed January, 9, 2023.
- Hicks CW, Selvin E. Epidemiology of Peripheral Neuropathy and Lower Extremity Disease in Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Aug 27;19(10):86.
- Hicks CW, Wang D, Matsushita K, et al. Peripheral Neuropathy and All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in U.S. Adults : A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Feb;174(2):167-74.
- Ziegler D, Reljanovic M, Mehnert H, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy in Germany: current evidence from clinical trials. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1999;107(7):421-30.
- Nguyen N, Takemoto JK. A Case for Alpha-Lipoic Acid as an Alternative Treatment for Diabetic Polyneuropathy. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2018;21(1s):177s-91s.
- Agathos E, Tentolouris A, Eleftheriadou I, et al. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on symptoms and quality of life in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. J Int Med Res. 2018 May;46(5):1779-90.
- El-Nahas MR, Elkannishy G, Abdelhafez H, et al. Oral Alpha Lipoic Acid Treatment for Symptomatic Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Study. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020;20(9):1531-4.
- Elbadawy AM, Abd Elmoniem RO, Elsayed AM. Alpha lipoic acid and diabetes mellitus: potential effects on peripheral neuropathy and different metabolic parameters. Alexandria Journal of Medicine. 2021;57(1):113-20.
- Karalis DT, Karalis T, Karalis S, et al. The Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and the Upcoming Depressive Disorders of Type II Diabetics. Cureus. 2021 Jan 18;13(1):e12773.
- Available at: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/peripheral-neuropathy#:~:text=The%20most%20common%20type%20of,as%20burning%20pain%20or%20paralysis. Accessed January, 9, 2023.
- Deli G, Bosnyak E, Pusch G, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: diagnosis and management. Neuroendocrinology. 2013;98(4):267-80.
- Available at: https://www.statpearls.com/articlelibrary/viewarticle/25827. Accessed January, 12, 2023.
- Hicks CW, Wang D, Windham BG, et al. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy defined by monofilament insensitivity in middle-aged and older adults in two US cohorts. Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 27;11(1):19159.
- Staff NP, Windebank AJ. Peripheral neuropathy due to vitamin deficiency, toxins, and medications. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2014 Oct;20(5 Peripheral Nervous System Disorders):1293-306.
- Kamitani F, Nishioka Y, Noda T, et al. Incidence of lower limb amputation in people with and without diabetes: a nationwide 5-year cohort study in Japan. BMJ Open. 2021 Aug 17;11(8):e048436.
- Agashe S, Petak S. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2018 Oct-Dec;14(4):251-6.
- Serhiyenko VA, Serhiyenko AA. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy: Risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. World J Diabetes. 2018 Jan 15;9(1):1-24.
- Data on file.
- Packer L, Cadenas E. Lipoic acid: energy metabolism and redox regulation of transcription and cell signaling. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2011 Jan;48(1):26-32.
- Golbidi S, Badran M, Laher I. Diabetes and alpha lipoic Acid. Front Pharmacol. 2011;2:69.
- Ansar H, Mazloom Z, Kazemi F, et al. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on blood glucose, insulin resistance and glutathione peroxidase of type 2 diabetic patients. Saudi Med J. 2011 Jun;32(6):584-8.
- Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564301/#!po=91.6667. Accessed 12/05/2022,
- Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/mental-health.html. Accessed January, 12, 2023.
- Serhiyenko VA, Serhiyenko LM, Sehin VB, et al. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on arterial stiffness parameters in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Endocr Regul. 2021 Dec 7;55(4):224-33.
- Namazi N, Larijani B, Azadbakht L. Alpha-lipoic acid supplement in obesity treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Clin Nutr. 2018 Apr;37(2):419-28.
- Carlson DA, Smith AR, Fischer SJ, et al. The plasma pharmacokinetics of R-(+)-lipoic acid administered as sodium R-(+)-lipoate to healthy human subjects. Altern Med Rev. 2007 Dec;12(4):343-51.
- Mrakic-Sposta S, Vezzoli A, Maderna L, et al. R(+)-Thioctic Acid Effects on Oxidative Stress and Peripheral Neuropathy in Type II Diabetic Patients: Preliminary Results by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance and Electroneurography. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:1767265.