Life Extension Magazine®
Our skin contains natural moisturizing oils known as ceramides.
When we’re young, they keep skin firm, moist, and wrinkle-free.
But with age, ceramide production declines, resulting in dry, sagging skin and wrinkling.1,2
Pollution and exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation accelerate this skin aging process.3
Researchers have found ways to prevent and reverse some of this damage with oral ceramides and herbal extracts.
Oral ceramides derived from rice are thought to work internally to boost production of ceramides in skin, promoting a more hydrated, youthful appearance.4,5
Additionally, researchers have also identified four herbal extracts that work together to mitigate skin aging caused by pollution and UV radiation.6
In a clinical trial, 96% of participants taking the herbal extracts had a significant reduction in wrinkle depth.6
Taken orally, these nutrients provide a strategic approach to rejuvenate skin and protect against environmental damage.
Ceramides Stop Skin Aging
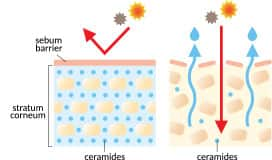
Ceramides can be thought of like the mortar that holds skin-cell bricks together.
Internal ceramide production declines as we age. This decreases the skin’s moisture barrier, resulting in thinning, wrinkles, dryness, roughness, and even increased risk of infection.1,7-12
Ceramides have been added to some skin creams since the early 1990s. But because topically applied ceramides do not reach deeper skin layers, their effects are generally modest.12,13
To address this problem, scientists developed plant-derived ceramides—or phytoceramides—that can be taken orally. These lipids are thought to boost the production of ceramides in the skin.
Researchers have now achieved clinical success by using ceramides from a non-genetically modified rice extract that is gluten- and allergen-free.4,5
Taken orally, these rice-derived phytoceramides work from the inside out to hydrate, smooth, and rejuvenate skin all over the body.4,5
Herbal Extracts Defend Against External Dangers
Age isn’t the only factor driving skin damage.
External factors like environmental pollutants and UV radiation from the sun can degrade the skin’s structural integrity, reducing skin firmness and elasticity. That leads to wrinkling and fine lines.3,14
In addition to inducing oxidative stress and inflammation, pollutants cause overexpression of the protein aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR).
AhR overactivation increases the expression of genes responsible for oxidative stress, inflammation, immunosuppression, pigmentation, skin cancer, and premature skin aging.6,14
Researchers have identified four herbal extracts that, when taken orally, protect against the damaging effects of pollution and UV exposure as follows:6
- Rosemary,
- Olive leaf,
- Lippia citriodora (lemon verbena) leaf, and
- Sophora japonica (Japanese pagoda tree) leaf.
These extracts have been shown in a clinical study to improve skin health and deliver substantial protection against pollutants and UV radiation.6
In vitro studies show that the extracts inhibit the overactivation of the AhR receptor that causes premature skin aging and other skin-damaging effects.6
The abilities of rice ceramides and this herbal blend to block and even reverse skin aging has been validated in human trials.
Improve Skin Hydration and Barrier Function
Scientists set out to test the effect of rice-derived ceramides on skin barrier function, the ability to retain moisture and protect against external threats.4
They enlisted 123 healthy volunteers with dry skin. Every day for 12 weeks, subjects took either rice extract providing ceramides or a placebo.
Investigators measured water loss that occurs when water passes from the skin’s middle layer to the outer layer and evaporates. This test is used as a measure of the skin’s barrier function.
In as few as four weeks, subjects taking the rice extract had significant reduction in water loss through the skin in nearly all body areas, compared to those taking a placebo.4
A second clinical trial was conducted on patients (mean age: 30.5 years) with mild atopic dermatitis, or eczema. This skin disease is characterized by impaired skin barrier function and a reduction in ceramide content, and leads to patches of itchy, dry skin.5
Every day for four weeks, the treatment group took a rice extract providing ceramides.
The placebo group had significant water loss over the course of the study, resulting in decreased water content in the outer layer of the skin.5
Those supplementing with the rice extract reduced their water loss by more than 30% compared to the placebo group. This was seen in visual improvements to skin appearance.5
Reducing Wrinkles
Researchers next tested the effectiveness of the blend of herbal extracts in guarding against environmental pollutants.
The combination consisted of:6
- Rosemary extract,
- Olive extract,
- Lippia citriodora extract, and
- Sophora japonica extract.
The researchers enlisted 100 women (aged 35-65 years), half of whom had sensitive skin.
The treatment group took 250 mg of the blend orally for 12 weeks. The researchers measured an exhaustive list of factors, such as skin moisture, radiance, and smoothness to evaluate the overall look and health of skin.6
More than 90% of treated volunteers had significant improvement in all of the measures.6
The herbal blend smoothed and softened skin, significantly reduced wrinkle depth, and improved skin elasticity and firmness—beginning in just 15 days.6
Compared to a placebo, after 12 weeks of treatment, the group taking the herbal extracts had:6
- A 10-fold greater decrease in wrinkle depth,
- A 3-fold improvement in skin moisture,
- 5 times the skin brightness or radiance,
- 2.5 times more lightening of dark spots,
- A nearly 5-fold reduction in water loss, and
- An 18-fold greater increase in skin smoothness.
These improvements in skin appearance are likely due to the reduction in water loss, which indicates a clear improvement in the skin barrier function.
A strengthened barrier function means pollutants are less able to penetrate to the deeper layers of the skin to cause damage.
Lab studies show that this blend completely inhibits the pollution-induced increase in the expression of the AhR receptor, which can cause pigmented spots, inflammation, and oxidative stress.6,14
What you need to know
Keep Skin Healthy and Strong

- Ceramides are natural oils that keep our skin hydrated and healthy. As we age, our bodies produce fewer ceramides, leading to wrinkles, dryness, and other signs of skin aging.
- Scientists have developed rice-derived ceramides. Taken orally, they have been shown to restore the skin’s vital barrier function and youthful skin hydration.
- External factors like environmental pollutants and exposure to UV radiation also accelerate skin aging.
- A blend of four herbal extracts (from rosemary, olive leaf, lemon verbena leaf, and Japanese pagoda tree leaf) defends the skin against the damaging effects of pollution and UV exposure.
- Vitamin C provides multiple benefits to skin health, such as promoting collagen formation and reducing dark-spot appearance.
- These ingredients support a healthy, hydrated, and more youthful-looking skin.
Vitamin C Offers Added Support
Vitamin C offers additional benefits for skin health.
In studies, vitamin C has been shown to:15-17
- Promote formation of collagen, the skin’s main structural protein,
- Reduce DNA damage in the skin,
- Scavenge harmful free radicals, including oxidants from UV radiation,
- Improve skin antioxidant activity in just two weeks, and
- Inhibit melanin production, reducing the appearance of dark spots.
Most readers of this publication supplement with vitamin C based on compelling scientific findings of its ability to help maintain more youthful collagen levels.
Summary

Skin aging is caused by a variety of factors.
The age-related decrease in production of skin ceramides, combined with the damaging effects of pollutants and UV radiation, leads to wrinkles, dryness, and age spots.
Taken orally, rice-derived ceramides have been clinically shown to enhance the skin’s barrier function and boost overall skin hydration.
A blend of four herbal extracts protects against the destructive effects of pollution and UV exposure, improving the health and appearance of the skin.
Vitamin C offers a range of additional benefits to the skin, such as promoting collagen formation and reducing dark-spot appearance.
These ingredients, taken orally, can help hydrate, rejuvenate, and protect skin for a more youthful appearance. •
If you have any questions on the scientific content of this article, please call a Life Extension® Wellness Specialist at 1-866-864-3027.
References
- Wang Z, Man MQ, Li T, et al. Aging-associated alterations in epidermal function and their clinical significance. Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Mar 27;12(6):5551-65.
- Jonca N. Ceramides metabolism and impaired epidermal barrier in cutaneous diseases and skin aging: focus on the role of the enzyme PNPLA1 in the synthesis of ù-O-acylceramides and its pathophysiological involvement in some forms of congenital ichthyoses. Ocl. 2019;26:17.
- Burke KE. Environmental aging of the skin: new insights. Plastic and Aesthetic Research. 2020;2020:59.
- Hirakawa S, Sato A, Hattori, Y., Matsumoto T, et al. Dietary rice bran extract improves TEWL of whole body. Jpn . Pharmacol . Ther. 2013;41:1051-9.
- Myoceram. Myoceram Scientific Summary. Data on File. 2021.
- Zeropollution. Supplier data: Zeropollution. Data on File. 2021.
- Imokawa G, Abe A, Jin K, et al. Decreased level of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: an etiologic factor in atopic dry skin? J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Apr;96(4):523-6.
- Coderch L, Lopez O, de la Maza A, et al. Ceramides and skin function. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(2):107-29.
- Boireau-Adamezyk E, Baillet-Guffroy A, Stamatas GN. Age-dependent changes in stratum corneum barrier function. Skin Res Technol. 2014 Nov;20(4):409-15.
- Rabionet M, Gorgas K, Sandhoff R. Ceramide synthesis in the epidermis Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Mar;1841(3):422-34.
- Leveque JL, Corcuff P, de Rigal J, et al. In vivo studies of the evolution of physical properties of the human skin with age. Int J Dermatol. 1984 Jun;23(5):322-9.
- Yilmaz E, Borchert HH. Effect of lipid-containing, positively charged nanoemulsions on skin hydration, elasticity and erythema--an in vivo study. Int J Pharm. 2006 Jan 13;307(2):232-8.
- Asai S, Miyachi H. [Evaluation of skin-moisturizing effects of oral or percutaneous use of plant ceramides]. Rinsho Byori. 2007 Mar;55(3):209-15.
- Dupont E, Gomez J, Bilodeau D. Beyond UV radiation: a skin under challenge. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013 Jun;35(3):224-32.
- Placzek M, Gaube S, Kerkmann U, et al. Ultraviolet B-induced DNA damage in human epidermis is modified by the antioxidants ascorbic acid and D-alpha-tocopherol. J Invest Dermatol. 2005 Feb;124(2):304-7.
- Lauer AC, Groth N, Haag SF, et al. Dose-dependent vitamin C uptake and radical scavenging activity in human skin measured with in vivo electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2013;26(3):147-54.
- Pullar JM, Carr AC, Vissers MCM. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients. 2017 Aug 12;9(8):866.

