
What are the Benefits of Omega-7?
Published: December 2021
Many of us know that omega-3 fatty acids are terrific for cardiovascular health, but there’s a “new” omega in town that’s been surging in popularity: omega-7 fatty acids.
Studies show that a type of omega-7 called palmitoleic acid offers a wide range of health benefits, ranging from heart to skin health support to maintaining already-healthy blood sugar levels, encouraging a healthy inflammatory response and more!
So how can you make sure you’re getting enough of this healthy fat, and should you take an omega-7 supplement? Let’s dive in!
What is omega-7?

Like omega-3, omega-7 is a type of fatty acid. These subunits or “building blocks” of the fat in our bodies and the foods we eat help us efficiently absorb nutrients like vitamins from our diet, help maintain our metabolism, and keep us energized. Supplementing with omega-7 fatty acids is an excellent way to complement the heart-friendly benefits of fatty acids, like omega-3s EPA and DHA.
Palmitoleic acid is the most abundant type of omega-7 fatty acids; it’s present in tissues throughout the body, particularly the liver. Emerging research reveals this monounsaturated fatty acid offers many health-promoting benefits.
In fact, omega-7 caught researchers’ attention when it showed its ability to act as a hormone in the body and help support healthy metabolism, meaning that it’s a lipokine. This means omega-7 can detach from fatty tissue and have a positive metabolic effect on organs, benefiting the skin, heart and mucous membranes.
Above all else, it gets top marks for its ability to inhibit inflammation to support whole-body health.
What does omega-7 do for you?

There are five specific ways omega-7 can benefit your health:
5 omega-7 benefits
1. Healthy from head-to-toe
Research links healthy serum levels of omega-7 with supporting healthy C-reactive protein levels and promoting a healthy inflammatory response. Omega-7 helps support digestion, liver health and overall health at a cellular level.
2. Heart-healthy fatty acid
Clinical research shows omega-7 supports a healthy heart by maintaining already-healthy cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Studies also show that eating more omega-7-rich foods or supplementing with palmitoleic acid is associated with supporting already-healthy lipoprotein—HDL “the good cholesterol” and LDL “the bad cholesterol”—blood levels.
3. Boosts collagen production
Omega-7 promotes collagen production, an essential protein for healthy skin, hair and nails.
4. Healthy weight
In preclinical studies, omega-7 was shown to influence healthy fat metabolism and inhibit the size of fat cells and amount of overall fat. Studies also show omega-7 promotes healthy fat metabolism, prompting the body to use it for energy production. This healthy fat also encourages already-healthy blood sugar levels and promotes feelings of satiety—which are vital components of healthy weight management.
5. Eye comfort
In a preclinical study, subjects who took omega-7-rich sea buckthorn pulp oil orally encouraged healthy eye lubrication and tear production.
Explore Our Best Heart Health Supplements
Omega-3 vs. Omega-7
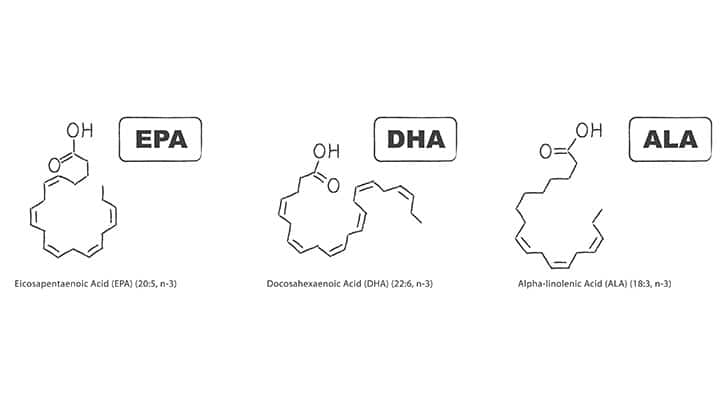
Omega-3 and omega-7 are both fatty acids, but they aren’t quite the same. So, what’s the difference?
Both omega-3 and omega-7 are beneficial to the body, but in somewhat different ways. Omega-3 benefits the heart, brain and joints, and omega-7 is well-known for supporting a healthy response to inflammation.
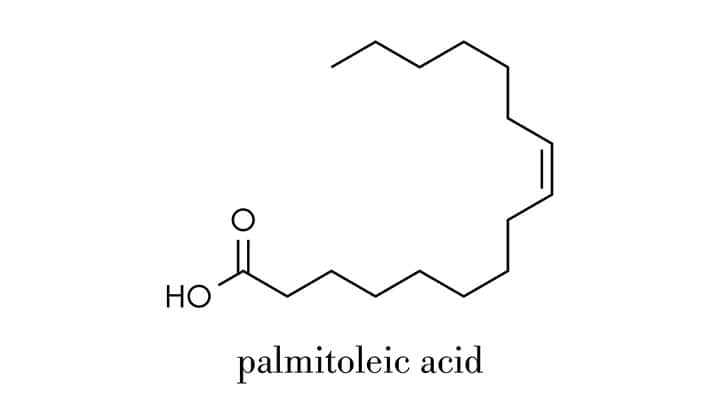
Where do the numbers “3” and “7” come from? Fatty acids consist of a straight chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms attached by single or double (rarely triple) bonds. The number next to the fatty acid’s name, like omega-3 or omega-7, shows where the saturation occurs within the chain. Omega-3 fatty acids have double bonds three carbon atoms from the end of the chain. And, you guessed it! Omega-7s have a double bond seven carbon atoms from the end of the chain.
Another difference is that omega-3 fatty acids have three double bonds, making them polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs). Omega-7s only have one double bond, so they are monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs).
Is omega-7 a fish oil?
The term “fish oil” is used interchangeably with omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, which are well-known for their brain and heart benefits. You can’t really use the words “fish oil” in place of omega-7, though. That’s because while you’ll find omega-7 fatty acids in some fish oils, they are not the same as the omega-3s.
However, omega-7 does complement omega-3 benefits. So, it’s a good idea to take them both together as part of your supplement plan.
What is the best source of omega-7?

Your body can make omega-7 fatty acids from other nutrients. That’s why it’s essential to have balanced and nutrient-rich meals. You’ll find omega-7s in fatty foods like:
Salmon
Anchovies
Macadamia nuts
Avocados
Sea buckthorn
If it’s not feasible for you to consume enough fish, or if macadamia nuts aren’t your thing, then speaking with your healthcare provider can help you find ways to complement your lifestyle choices and ensure you’re getting omega-7 benefits.
References
- Chavaro-Ortíz, I. Lidia, et al. “Trans-Palmitoleic Acid Reduces Adiposity Via Increased Lipolysis in a Rodent Model of Diet-Induced Obesity.” Br. J Nutr., May 2021, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33958011/
- Cunningham, Eleese, RDN. “What Are n-7 Fatty Acids and Are There Health Benefits Associated with Them?” Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, January 2015, https://www.jandonline.org/article/S2212-2672(14)01769-9/fulltext#relatedArticles
- Di Pasquale, G. Mauro. “The Essentials of Essential Fatty Acids.” J Diet Suppl., 2009, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22435414/
- Dutchen, Stephanie. “What Do Fats Do in the Body?” National Institute of General Medical Sciences, December 2010, https://www.nigms.nih.gov/education/Inside-Life-Science/Pages/what-do-fats-do-in-the-body.aspx
- Frigolet, E. María et al. “The Role of the Novel Lipokine Palmitoleic Acid in Health and Disease.” Adv Nutr., January 2017, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5227969/
- Halonen, I. Jaana, Ph.D. et al. “Outdoor Temperature Is Associated with Serum HDL and LDL.” Environ Res.,February 2011, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4437587/
- Hassett, R. Patrick et al. “Habitat Temperature Is an Important Determinant of Cholesterol Contents in Copepods.” J Exp Biol., January 2009, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2749703/
- Hu, Wei et al. “A Review of Biological Functions, Health Benefits, and Possible de Novo Biosynthetic Pathway of Palmitoleic Acid in Macadamia nuts.” Journal of Functional Foods, November 2019, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S175646461930444X?casa_token=bxKn939E8ikAAAAA:Qhhgebe9Q60Yv3IJR7GFKO5MX1mKFlVoh6zPqeApylm7YTmoT8IZitmx85YeUmwJU15dx3MgSis
- Järvinen, Riika, L et al. "Effects of oral sea buckthorn oil on tear film Fatty acids in individuals with dry eye." Cornea, September 2011, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21832964/
- Kimura, Yuki et al. “Restoration of Tear Secretion in a Murine Dry Eye Model by Oral Administration of Palmitoleic Acid.” Nutrients, April 2017, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28379171/
- Kouda, Katsuyasu et al. “Negative Relationships Between Growth in Height and Levels of Cholesterol in Puberty: A 3-Year Follow-Up Study.” Int J Epidemiol., December 2003, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14681284/
- Kremmyda, Stella Lefkothea, et. al. “Fatty Acids as Biocompounds: Their Role in Human Metabolism, Health and Disease: A Review. Part 2: Fatty Acid Physiological Roles and Applications in Human Health and Disease.” Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomjuc Czech Repub., September 2011, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22286806/
- Marsiñach, Solà Marta et al. “The Impact of Sea Buckthorn Oil Fatty Acids on Human Health.” Lipids Health Dis. June 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6589177/
- Sedes, Lauiane, et al. “Cholesterol: A Gatekeeper of Male Fertility?” Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).,July 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6060264/
- Song, In-Bong, et. al. “Omega-7 Inhibits Inflammation and Promotes Collagen Synthesis Through SIRT1 Activation.” Applied Biological Chemistry, June 2018, https://applbiolchem.springeropen.com/articles/10.1007/s13765-018-0377-1
- Tall, R. Alan, et al. “Cholesterol, Inflammation and Innate Immunity.” Nat Rev Immunol., February 2015, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4669071/
- Weimann, Eleine, et al. “Topical Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Palmitoleic Acid Improves Wound Healing.” PLoS One, October 2018, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30307983/
- Yang, Zhi-Hong, Jiro, Takeo, Masashi Katayama. “Oral Administration of Omega-7 Palmitoleic Acid Induces Satiety and the Release of Appetite-Related Hormones in Male Rats.” Appetite, June 2013, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23376733/
- “Essential Fatty Acids.” Data on file.
- “Omega 3-6-7-9— What’s the Difference?” MDCurrent India, http://mdcurrent.in/patients/omega-3-7-6-9-whats-the-difference/
Always be in the know!
Access the latest deals, wellness news, expert health tips & more!






